|
GR9677 #30
|
|
|
|
|
Alternate Solutions |
carle257
2010-04-04 20:28:24 | 3 equations to write out that describe the system.
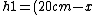 +5cm)
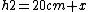
 - x = x) to equate the potentials on each side. (4 times heavier fluid.) to equate the potentials on each side. (4 times heavier fluid.)
You can then simply solve this very rapidly to get x=10 and then the heights are 2:1. | 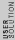 |
|
|
Comments |
SurpriseAttachyon
2015-10-22 15:34:53 | I definitely agree with the original solution, but the ETS should really be more careful with their wording (I\\\\\\\'ve felt this way on many many of their questions).\\\\r\\\\n\\\\r\\\\nThe problem as stated is technically wrong because the tube is curved. The equation  is only approximately right.\\\\r\\\\n\\\\r\\\\nEven just saying \\\\\\\"What is the approximate ratio...\\\\\\\", would suffice. is only approximately right.\\\\r\\\\n\\\\r\\\\nEven just saying \\\\\\\"What is the approximate ratio...\\\\\\\", would suffice. |  | epuma
2013-07-21 10:15:10 | A simple conceptual solution:rnrnModel the system as a two-mass balance, where the mass of the right arm liquid must equal the mass of the left arm liquid for the system to remain at rest. We must find the liquid heights which give equal mass in each arm after the dense liquid has been added to the left arm. (We can ignore the bottom U shape, and I'll refer to masses PER cross sectional area to clean up units.) rnrnThe total mass of the initial water per cross sectional area is 40g, 20g in each arm. Now we add 5cm of liquid 4 times as dense, which amounts to an additional 20g, for a total of 60g of liquid.rnrnThe mass equalization condition requires 60g/2 =30g in each arm. In the right arm, this amounts to 30cm of water (remember, the water is 1g/cm). In the left arm, the remaining 10cm of water and the added 5cm of dense liquid yield a left arm height of 15cm.rnrnThe ratio h2/h1 is thus 30cm/15cm or (C) 2/1.rnrnrnrn |  | anum
2010-11-02 01:14:56 | why can't it be 1/1? i mean the fall of liquid in one tube is equal to the rise of liquid in the other tube . isn't it? |  | anum
2010-11-02 01:07:06 | why can't it be 1/1? i mean the fall of liquid in one tube is equal to the rise of liquid in the other tube . isn't it?
anum
2010-11-12 10:36:22 |
plz ignore the last comment i get it. densities r different and even in the diagram the heights are different
|
|  | carle257
2010-04-04 20:28:24 | 3 equations to write out that describe the system.
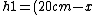 +5cm)
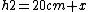
 - x = x) to equate the potentials on each side. (4 times heavier fluid.) to equate the potentials on each side. (4 times heavier fluid.)
You can then simply solve this very rapidly to get x=10 and then the heights are 2:1.
matweiss
2010-10-02 17:42:06 |
this is a GREAT solution, and the one I was trying to come up with in my head but couldn't
notice that the first two equations don't even matter at all, just the third one. this gives you 4(5cm)-x=x . which gives you 20cm=2x which igives you x=10 cm
good stuff
|
psitae
2016-10-27 04:07:49 |
very good! you used the fact that water doesn\'t compress to realize that the two water levels have the same distance to the 20 cm point!
|
|  | phys2718
2008-10-06 13:44:57 | This problem doesn't make sense physically. When you add the denser liquid to the water it will form at the bottom of the tube rather than the top. Just try adding water to oil.
HaveSpaceSuit
2008-10-16 19:27:18 |
The question says that the liquid is immiscible, so it can't mix with the water. Thus, it just acts as a weight on the top of the water.
|
adjwilley
2009-11-05 17:52:28 |
Water and oil are immiscible.
|
TubbyBeef
2016-10-26 22:44:59 |
You are correct. A fluid with density half that of steel would not float freely in water. \r\n\r\nThe notion that they are imiscible and this prevents the more dense fluid from sinking relies on the tube being narrow.. narrow enough that surface tension effects can dominate over buoyancy effects and the Rayleigh–Taylor instability present. \r\n\r\nThere is a reason we don\'t use capillary tubes as manometers. :-/
|
|  | hoyas08
2008-06-22 16:53:38 | I think one can also do this problem conceptually with only a bit of math. Since the liquid is 4 times denser than water, adding 5 cm of liquid to the left must be balanced by having 20 cm more water on the right side than on the left side at final equilibrium. This is the case when you push 10 cm of water from the left side over to the right, giving you:
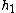 = 20 cm - 10 cm + 5 cm = 15 cm = 20 cm - 10 cm + 5 cm = 15 cm
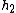 = 20 cm + 10 cm = 30 cm = 20 cm + 10 cm = 30 cm
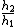 = = 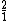
Saved me some algebra, at least.
cpstrehlow
2008-11-06 16:02:56 |
I solved this problem by equating 5 cm of immiscible liquid (four times as dense as water), with 20 cm of water. adding twenty cm of water to one side gives 40 cm on one side and 20 on the other. to balance out, there must be 30 cm on each side. knowing that h1 must be 15, it takes no algebra to see that the ratio is 2.
|
jmason86
2009-10-09 11:39:01 |
hoyaso: awesome solution. I was trying to do something similar, but gave up because of time pressure. Nice to see someone else thinking this thing through simply :)
|
|  | grae313
2007-10-31 12:14:00 | You can also equate the total pressures on each side using 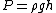 (this is exactly the same as what you did except this uses the base of the tube as the equipotential line, I found this more intuitive) (this is exactly the same as what you did except this uses the base of the tube as the equipotential line, I found this more intuitive)
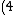g(5) + (1)g(h_1 - 5) = (1)g(h_2))
and then use the face that 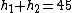 to arrive at the same answer to arrive at the same answer |  | antithesis
2007-10-04 15:20:32 | Technically, there is also the pressure of the air, but both sides are open, so it cancels on both sides. |  |
|
|
|
|
The Sidebar Chatbox...
Scroll to see it, or resize your browser to ignore it... |
|
|
|
