|
GR8677 #56
|
|
|
Problem
|
|
 |
Quantum Mechanics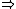 }Expectation Value }Expectation Value
Recall the following result of the Born Assumption,
where the above yields the average value of Q---i.e., the expectation value.
|
|
|
Alternate Solutions |
| There are no Alternate Solutions for this problem. Be the first to post one! |
|
|
Comments |
ernest21
2019-08-23 02:03:17 | Truth is, I couldn\'t remember offhand what the Born approximation was, either; now it comes back to me. Moral of the story; under a \"No Guesses\" strategy, I couldn\'t gain the point. parallel parking game |  | flyboy621
2010-11-14 21:44:39 | What confuses me about this problem is that I understand the "mean value" and the "expectation value" to be different things. I know "expectation value" would be correct here, but I'm not so sure about "mean value."
I just chose (C) because it can't be any of the other answers.
mpdude8
2012-04-19 14:44:19 |
Picking an answer because it couldn't be any of the others is a great GRE strategy, though.
|
|  | FortranMan
2008-10-27 14:34:50 | So when they say "corresponding to" they mean that Q is proportional to x, rather than say Q is proportional to some operation like  ? ?
a19grey2
2008-11-03 22:33:24 |
They don't mean proportional in any way. They mean that Q IS some operator like  . .
Also, ETS is trying to trick you here, because when x is the position of the particle, then the operator Q = x. In this special case, the value they give IS the spatial overlap of Q with the wavefunction. This is only true though, when x is the position value and not in other, mor egeneral cases, as the problem wants us to consider.
Whereas, the equation given is ALWAYS the expected value of the observable quantity (C).
|
flyboy621
2010-11-14 21:41:49 |
If the operator Q corresponds to the observable quantity x, then the eigenvalues of Q (operating on the wavefunction) are the possible results you can get when you measure x.
|
|  |
|
|
|
|
The Sidebar Chatbox...
Scroll to see it, or resize your browser to ignore it... |
|
|
|
