|
GR8677 #2
|
|
|
Problem
|
|
 |
Mechanics }Vector }Vector
While there may be a more quantitative solution, the simplest solution is qualitative, based on elementary vector addition and knowledge of the force center.
The problem states that the object orbits the Earth in a perfect circle, initially. This means that the initial velocity (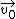 ) is perpendicular to the vector pointing to the earth center ( ) is perpendicular to the vector pointing to the earth center (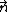 ), i.e., it's tangent to the circular path. This is the condition for uniform circular motion (the centripetal acceleration is due to the Gravitational Law). ), i.e., it's tangent to the circular path. This is the condition for uniform circular motion (the centripetal acceleration is due to the Gravitational Law).
After firing a missile straight to Earth center, its velocity gains an extra normal component (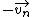 ), equal and opposite to the velocity of the missile fired to Earth. Thus, its trajectory would deviate from the circular trajectory. ), equal and opposite to the velocity of the missile fired to Earth. Thus, its trajectory would deviate from the circular trajectory.
Because the only source of acceleration comes from the Earth center, 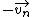 , which is parallel to the centripetal acceleration provided by the Earth, will eventually go to 0. Recall that acceleration does not effect velocity components in the perpendicular direction (to wit: a projectile fired on Earth has the same constant , which is parallel to the centripetal acceleration provided by the Earth, will eventually go to 0. Recall that acceleration does not effect velocity components in the perpendicular direction (to wit: a projectile fired on Earth has the same constant 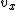 , but its , but its 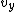 changes). There will thus always be a (nearly constant) tangential velocity, even at the perigees. However, changes). There will thus always be a (nearly constant) tangential velocity, even at the perigees. However, 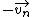 will go to 0 at the perigees. The tangential velocity will remain more-or-less constant, so that instead of spiraling inwards, the path becomes an ellipse, as will go to 0 at the perigees. The tangential velocity will remain more-or-less constant, so that instead of spiraling inwards, the path becomes an ellipse, as 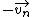 is restored at the apogees and zero'ed at the perigees. is restored at the apogees and zero'ed at the perigees.
(In a more down-to-earth form, this problem is essentially a projectile firing question with no numerical work involved.)
|
|
|
Alternate Solutions |
TheThillyOne
2010-11-06 21:10:02 | Here's an easy way to see it. The perturbation is slight, so we end up either with a circle again or an ellipse. The only other possible solutions to the orbital equation are parabolas and hyperbolas, which correspond to unbound energies at least twice as high as orbital energy and a small perturbation wont get us up there.rnrnThe force is perpendicular to the velocity, so angular moment must be conserved (no torque). For a given object, each circular orbit corresponds to a different angular momentum.rnrnGM/r^2=v^2/r ---> V=Sqrt(GM/r)rnL(r)_circularorbit=mrv=mSqrt(GMr)rnrnSo the orbit cannot be circular. It must be an ellipse. |  | angiep
2005-11-09 07:48:42 | I disagree with your answer. It's a question about the classification of orbits. You need a graph of the effective potential. I found some stuff on it here: http://www.bun.kyoto-u.ac.jp/~suchii/eff.potent.html. I like how it's treated better in Goldstein (classical mechanics, i have the 3rd ed). Basically, the only orbits possible with an inverse square force law are a hyperbola, parabola, ellipse, or circle. Circular only occurs at a particular radius. A perturbation from there gives you a slightly higher energy, and you are in a region of an elliptical orbit.
I like your site! Thanks! |  |
|
|
Comments |
ernest21
2019-08-10 03:09:37 | I am preparing for general and physics gre . I got a lot of information for physics but not for general. so anybody will help me . Thanks. phrase wheel of fortune
danielsw98667
2019-10-18 06:32:55 |
Because the perturbation is slight, it has to be an ellipse. Jewelry Dayton Ohio
|
|  | fredluis
2019-08-08 12:46:07 | It can also be solved by noting the units and realizing that it cannot be zero or g. That leaves only D. carpet cleaner |  | joshuaprice153
2019-08-08 04:41:28 | Do you have a spam issue on this website; I also am a blogger, and I wanted to know your situation; many of us have developed some nice methods, and we are looking to trade methods with others, why not shoot me an e-mail if interested. power washing |  | casseverhart13
2019-07-01 03:24:14 | Good problem to solve.... I think I may be a little to late to vote though.... www.appliancerepairsoforlando.com/hunterscreek |  | camarasi
2017-10-24 15:46:26 | The ISS is essentially in a circular orbit. Due to drag forces of the atmosphere, it loses tangential velocity and therefore \'spirals\' in towards earth. To counteract this, it must be boosted back up to within its altitude limits. This is done by two thrusts at opposite ends of the orbit: any delta-v you introduce must be cancelled out for the orbit to remain circular. It follows that if you have a single boost from a circular orbit, it becomes elliptical. |  | socolenco_
2015-09-03 20:44:13 | \"After firing a missile straight to Earth center, its velocity gains an extra normal component 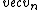 , equal and opposite to the velocity of the missile fired to Earth.\"\r\n\r\nThe satellite is not firing a missile, but a control jet. Anyway, if a missile helps you think better about this problem, then you have to keep in mind that it has a mass m, which means a momentum mv that should be equal and opposite to the momentum of the satellite (M-m)V. \r\n\r\nSo, its normal component , equal and opposite to the velocity of the missile fired to Earth.\"\r\n\r\nThe satellite is not firing a missile, but a control jet. Anyway, if a missile helps you think better about this problem, then you have to keep in mind that it has a mass m, which means a momentum mv that should be equal and opposite to the momentum of the satellite (M-m)V. \r\n\r\nSo, its normal component 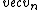 cannot be equal and opposite to the velocity of the missile fired to Earth. cannot be equal and opposite to the velocity of the missile fired to Earth. |  | socolenco_
2015-09-03 20:27:31 | \"After firing a missile straight to Earth center, its velocity gains an extra normal component 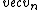 , equal and opposite to the velocity of the missile fired to Earth.\" \r\n\r\nThe satellite is not firing a missile, but a control jet. Anyway, if a missile helps you think better about this problem, then you have to keep in mind that it has a mass m, which means a momentum mv that should be equal and opposite to the momentum of the satellite (M-m)V. \r\n\r\nSo, its normal component , equal and opposite to the velocity of the missile fired to Earth.\" \r\n\r\nThe satellite is not firing a missile, but a control jet. Anyway, if a missile helps you think better about this problem, then you have to keep in mind that it has a mass m, which means a momentum mv that should be equal and opposite to the momentum of the satellite (M-m)V. \r\n\r\nSo, its normal component 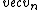 cannot be equal and opposite to the velocity of the missile fired to Earth. cannot be equal and opposite to the velocity of the missile fired to Earth. |  | 201210947
2014-07-04 07:07:58 | hellllllllllpppppppppppp!!!!!! |  | llama
2013-10-16 20:25:03 | Second question that kerbal space program has helped with, makes me feel slightly less bad about procrastinating with video games so much. |  | KRoss1024
2013-05-01 19:48:56 | You folks are missing the big picture. Kepler's laws are empirical facts. Whatever you think analytically must be subordinated to the simple fact that all bound orbits are elliptical with circular orbit as a special case. Any perturbation of a circular orbit that does not free the particle results in an elliptical orbit.
There is no time for analysis. The question is testing your knowledge of facts. |  | alhazen
2012-06-01 14:49:54 | Similar problem is given in the book of Taylor's Classical Mechanics. B part of of the problem 8.12 states that a small radial nudge will cause only small radial oscillations; this tells us that E answer is correct. But it is very odd that ETS's official answer sheet says A answer is right. Any thoughts?
alhazen
2012-06-01 15:05:43 |
But the period of oscillations is equal to the planet's orbital period, not "many radial oscillations per revolution". Then what is the right answer?
|
fuzics
2012-09-29 15:16:21 |
If the radial oscillations have period equal to the period of one revolution, the satellite will trace out an ellipse.
|
|  | natanael2
2012-01-17 17:30:23 | It's a example of Marion & Thorton (classical dynamics). In chapter 8 they discussed central-force motion. On the section 8.10 (with 8.6), they solve this problem in a straightforward way. The correct choose is E. |  | TheThillyOne
2010-11-06 21:10:02 | Here's an easy way to see it. The perturbation is slight, so we end up either with a circle again or an ellipse. The only other possible solutions to the orbital equation are parabolas and hyperbolas, which correspond to unbound energies at least twice as high as orbital energy and a small perturbation wont get us up there.rnrnThe force is perpendicular to the velocity, so angular moment must be conserved (no torque). For a given object, each circular orbit corresponds to a different angular momentum.rnrnGM/r^2=v^2/r ---> V=Sqrt(GM/r)rnL(r)_circularorbit=mrv=mSqrt(GMr)rnrnSo the orbit cannot be circular. It must be an ellipse. |  | TheThillyOne
2010-11-06 21:09:29 | Here's an easy way to see it. The perturbation is slight, so we end up either with a circle again or an ellipse. The only other possible solutions to the orbital equation are parabolas and hyperbolas, which correspond to unbound energies at least twice as high as orbital energy and a small perturbation wont get us up there.rnrnThe force is perpendicular to the velocity, so angular moment must be conserved (no torque). For a given object, each circular orbit corresponds to a different angular momentum.rnrnGM/r^2=v^2/r ---> V=Sqrt(GM/r)rnL(r)_circularorbit=mrv=mSqrt(GMr)rnrnSo the orbit cannot be circular. It must be an ellipse. |  | TheThillyOne
2010-11-06 21:08:53 | Here's an easy way to see it. The perturbation is slight, so we end up either with a circle again or an ellipse. The only other possible solutions to the orbital equation are parabolas and hyperbolas, which correspond to unbound energies at least twice as high as orbital energy and a small perturbation wont get us up there.rnrnThe force is perpendicular to the velocity, so angular moment must be conserved (no torque). For a given object, each circular orbit corresponds to a different angular momentum.rnrnGM/r^2=v^2/r ---> V=Sqrt(GM/r)rnL(r)_circularorbit=mrv=mSqrt(GMr)rnrnSo the orbit cannot be circular. It must be an ellipse. |  | newbie
2010-10-18 09:44:09 | Why is D not an answer?
Many thanks for the owner as well as the fervent users...
Waiting for your insightful answers.
Dodobird
2010-11-04 18:06:00 |
A spiral is not a possible orbit for a body moving under the influence of gravity.
Because a spiral would eventually completely escape the gravitational field, it has a positive total energy. A uniqueness theorem of ordinary differential equations guarantees that a hyperbola is the only possible nonzero positive solution.
|
|  | newbie
2010-10-18 09:43:37 | Why is D not an answer?
Many thanks for the owner as well as the fervent users...
Waiting for your insightful answers. |  | Patrusfarr
2009-09-28 18:57:20 | Someone explain to me why it cannot possibly be a hyperbola. Is it because we said the words "slightly perturbed?" Given enough boost, an object will go into a hyperbolic orbit.
kroner
2009-09-28 19:35:14 |
Yeah that's right. To go from a circular orbit to a hyperbolic orbit you need to more than double the kinetic energy of the satellite, which is a big change in the context of any realistic Earth orbit.
|
|  | engageengage
2009-01-17 17:58:09 | The reason that it cannot be E is because a perturbation would cause oscillations to occur at the same frequency as the initial orbit. Therefore, it would not cause 'many' radial oscillations, but only one, per revolution. In fact, if you think about the inner and outer radii of a perturbed orbit where the radial oscillations match the orbital 'oscillations', you see that the orbit is actually ellipse.
It might be possible to do the derivation in a couple of minutes, if one is to know exactly what to look for. Consider the effective potential:
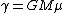
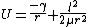
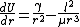
the stable orbit occurs when this quantity is zero, i.e., this is an equilibrium point.
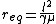
We take the second derivative, knowing that we can expand the potential using a taylor series, approximating the potential as a quadratic potential well. Here, the second derivative of the potential evaluated at the equilibrium point corresponds to the force constant, 'k' in a typical harmonic oscillator problem (write out the taylor series to see why).
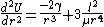
At 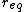 : :
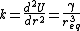
Now, we can easily deduce the the frequency of the oscillation, plugging in the value of gamma:
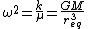
Finally, where T is the period:
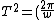^{2} = \frac{4\pi^{2}r_{eq}^{3}}{GM} )
This is just Kepler's Third Law for orbits! Therefore, any radial perturbation would cause the radial oscillations equal to the angular period. So, the answer cannot be E, and must be A |  | dcn
2008-03-26 07:59:22 | You have a typo in your explanation. I'm not the greatest speller but I think in the fourth paragraph, second sentence, it should be "affect" instead of "effect". Effect is a noun and is the result when something is affected, which is a verb. This is a great site. Thanks.
Setareh
2011-10-23 13:10:00 |
I am sure that effect is also a verb.. Check your dictionary.. And no need to mention that we mostly care about the physical concepts not dictation..
|
|  | climbing_evergreen@grephysics.net
2007-11-23 01:28:29 | |  | Richard
2007-11-02 09:30:28 | Right, I understand all that, but what is Goldstein talking about in Chapter 3.6?
Look at Figure 3.13. And there is this:
"If a circular orbit is stable, then a small increase in the particle energy above the value for a circular orbit results in only a slight variation of  about about 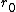 . It can be easily shown that for such small deviations from the circularity conditions, the particle execute a simple harmonic motion..." . It can be easily shown that for such small deviations from the circularity conditions, the particle execute a simple harmonic motion..."
So I would think to choose (E).
But I've only given Goldstein a cursory read, so I'm probably missing something. It seems that if you look at the potential curve, it's pretty obvious when you get a circular orbit (at the base where only one  is possible) and when you get an elliptical orbit (anywhere where you have a finite range of possible is possible) and when you get an elliptical orbit (anywhere where you have a finite range of possible  's, which occurs at total energy less than zero.) 's, which occurs at total energy less than zero.)
So how do I reconcile these two thoughts?
physicsisgod
2008-11-05 16:44:09 |
I think the solution to this confusion is that the oscillations in the orbit occur when we slightly perturb the radius, but we leave the kinetic energy constant. So really, we're increasing the energy of the particle by changing its potential energy (we move it in the gravitational field, but keep its momentum constant). In the case of this GRE problem, we are acutally adding to the particle's momentum, by giving it some radial velocity for a short period of time. I think this might be a better way to think about the difference.
|
alemsalem
2010-09-20 02:07:25 |
yes the particle will undergo simple harmonic motion in r but it will not undergo many oscillations in a revolution, this is always true for bounded orbits in an inverse square force when r goes from rmax to rmin and back again the angle will have changed by 2 pi.
|
|  | phillipkp
2006-04-30 09:42:27 | Check out section 8.7 in Marion and Thornton also.
kolahalb
2007-12-07 11:44:02 |
I would suggest something...
After a small perturbation,energy is more and we get no more circular orbit.For inverse square law forces,(and for F=-kr type of forces) we get stable noncircular orbits(which are closed).So,correct answer is (A)
Now why not (E)?I strongly suggest to refer to Atam P Arya's book.To have radial oscillation (and an ultimately closed trajectory) we must have
T(r)/T(theta) =a rational number.[The figure is a popular one---front cover page of Goldstein].
when the ratio=1,we get T(r)=T(theta) and ellipse results.That is what exactly happens in attractive inverse square alw force.
|
|  | angiep
2005-11-09 07:48:42 | I disagree with your answer. It's a question about the classification of orbits. You need a graph of the effective potential. I found some stuff on it here: http://www.bun.kyoto-u.ac.jp/~suchii/eff.potent.html. I like how it's treated better in Goldstein (classical mechanics, i have the 3rd ed). Basically, the only orbits possible with an inverse square force law are a hyperbola, parabola, ellipse, or circle. Circular only occurs at a particular radius. A perturbation from there gives you a slightly higher energy, and you are in a region of an elliptical orbit.
I like your site! Thanks!
sharpstones
2007-04-01 13:54:27 |
Just to add some more detail since this is an important concept to have down.
Classification of Orbits by total energy 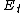
$E_t > 0 E_t = 0 E_t = 0 E_t < 0$ -> Elliptical Orbit E_t < 0$ -> Elliptical Orbit
-> special case 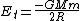
So changing your energy from a circular orbit will give you an ellipse... increase energy too much and you can eventually reach a hyperbolic orbit.
|
sharpstones
2007-04-01 13:56:12 |
Just to add some more detail since this is an important concept to have down.
Classification of Orbits by total energy 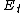
E_t > 0 Hyperbolic orbit
E_t = 0 Parabolic orbit
E_t < 0 Elliptical Orbit
-> special case 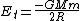
So changing your energy from a circular orbit will give you an ellipse... increase energy too much and you can eventually reach a hyperbolic orbit.
|
|  |
|
| Post A Comment! |
You are replying to:
The reason that it cannot be E is because a perturbation would cause oscillations to occur at the same frequency as the initial orbit. Therefore, it would not cause 'many' radial oscillations, but only one, per revolution. In fact, if you think about the inner and outer radii of a perturbed orbit where the radial oscillations match the orbital 'oscillations', you see that the orbit is actually ellipse.
It might be possible to do the derivation in a couple of minutes, if one is to know exactly what to look for. Consider the effective potential:
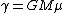
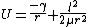
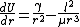
the stable orbit occurs when this quantity is zero, i.e., this is an equilibrium point.
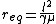
We take the second derivative, knowing that we can expand the potential using a taylor series, approximating the potential as a quadratic potential well. Here, the second derivative of the potential evaluated at the equilibrium point corresponds to the force constant, 'k' in a typical harmonic oscillator problem (write out the taylor series to see why).
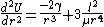
At 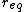 :
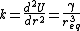
Now, we can easily deduce the the frequency of the oscillation, plugging in the value of gamma:
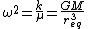
Finally, where T is the period:
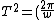^{2} = \frac{4\pi^{2}r_{eq}^{3}}{GM} )
This is just Kepler's Third Law for orbits! Therefore, any radial perturbation would cause the radial oscillations equal to the angular period. So, the answer cannot be E, and must be A |
Bare Basic LaTeX Rosetta Stone
|
LaTeX syntax supported through dollar sign wrappers $, ex., $\alpha^2_0$ produces 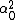 . .
|
| type this... |
to get... |
| $\int_0^\infty$ |
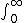 |
| $\partial$ |
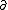 |
| $\Rightarrow$ |
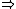 |
| $\ddot{x},\dot{x}$ |
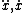 |
| $\sqrt{z}$ |
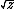 |
| $\langle my \rangle$ |
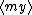 |
| $\left( abacadabra \right)_{me}$ |
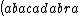_{me}) |
| $\vec{E}$ |
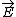 |
| $\frac{a}{b}$ |
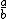 |
|
|
|
|
The Sidebar Chatbox...
Scroll to see it, or resize your browser to ignore it... |
|
|
|
