|
GR0177 #44
|
|
|
|
|
Alternate Solutions |
dipropon
2015-10-14 02:41:09 | I would argue, that the answer is C. 7E1 which is the expectation value of Energy operator , because the variance of Energy operator is zero. So it doesn\'t matter how many times (once,twice....million times) you measure the energy of the same state , you will get the expectation value.\r\n\r\nIf the variance of energy operator is were non zero then this argument wouldn\'t work. | 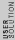 | uhurulol
2014-10-19 22:33:27 | Even the solutions here make it sound more complicated than it is. I have not yet taken quantum, so here's how to understand it if you have no quantum knowledge.
All that matters is the equation for 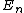 . Plug in 1 for this equation and obtain: . Plug in 1 for this equation and obtain:
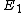 = = 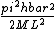 . .
Ergo, 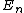 = = 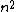 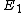 . .
Only choice D accommodates this, as it is the only integer square in the list (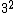 = 9). = 9).
Hope this helps. | 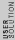 | ericimo
2007-11-01 15:05:07 | All you need to know is 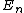 . The rest is given by ETS to try and make you overthink it and skip it. All you see is a scary quantum question when it's just monkey work. . The rest is given by ETS to try and make you overthink it and skip it. All you see is a scary quantum question when it's just monkey work.
It's apparent from the given 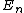 that that 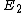 = = 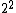 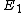 = 4 = 4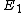 and equally apparent that and equally apparent that 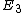 = 9 = 9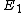 and so on. and so on.
If it's not obvious to you...plug and chug n=1,2,3..., and you see that D works for n=3 which is reason enough to choose it. |  |
|
|
Comments |
xana
2018-10-22 18:20:19 | 根据公式,显然有E2=4E1,E3=9E1\r\n平均能量会是1/14*E1+4/14*4E1+9/14*9E1=7E1\r\n然后操蛋的ETS只想问单次测量可能的值\r\n很好,那只有9E1可能,选D\r\n\r\nBy the formula, it is obviously that E2=4E1 and E3=9E1\r\nThe everage energy would be 1/14*E1+4/14*4E1+9/14*9E1=7E1\r\nBTW, the f---ing ETS just want to ask you the energy about \"a measurement\" could be\r\nAlright, only 9E1 is possible, so choose D.\r\n |  | francesco
2017-09-06 08:46:20 | Good morning guys, \r\nI gave a wrong answer as well, as I was tricked by the EV instead of focusing on measurement. So, thanks a lot to the users that opened my eyes pointing that out, I try to rephrase it in a more verbose way:\r\n\r\na. the state is a linear superposition of 3 eigenstates, but this just means that the only energy values I can obtain with an (ideal) measurement are E1, E2, E3 (that is, values belonging to the discrete spectrum of the energy operator). \r\n\r\nb. as a consequence of the result of the measurement (i.e. eigenvalue En), the state function will collapse into the eigenstate corresponding to En;\r\n\r\nc. averaging on many measurements, I will obtain E1, E2, E3 with the relative probabilities given by the probability amplitudes of the initial state, and not a value that is some weighted average value of E1, E2, E3.\r\nJust as, flipping a coin 1M times, I\'ll always obtain head or tail with a 50%-50% distribution, and not \"he-il\" or \"ta-ad\";\r\n\r\nd. is any of E1, E2, E3 a solution? Yes, and that\'s choice D\r\n\r\ne. 7E1 cannot be an answer because H|psi> != 7E1|psi>, or more generally, superposition of eigenfunctions is not eigenfunction itself (except the degenerate case);\r\n\r\nDoes it make sense to you/present any flaw somewhere?\r\n\r\nKeep up the good work and thanks for this site!\r\n\r\nFrancesco
francesco
2017-09-06 08:48:30 |
apologize for terrible formatting...
|
|  | physgre
2015-10-15 07:52:48 | 审题 |  | dipropon
2015-10-14 02:41:09 | I would argue, that the answer is C. 7E1 which is the expectation value of Energy operator , because the variance of Energy operator is zero. So it doesn\'t matter how many times (once,twice....million times) you measure the energy of the same state , you will get the expectation value.\r\n\r\nIf the variance of energy operator is were non zero then this argument wouldn\'t work.
dc771957
2016-10-08 16:58:04 |
The question asks which of the following is a possible measurement of energy for the state, not the average measurement for energy for the state. No matter how many times you measure the energy of this state, you will never get the expectation value, because it is not a possible energy eigenvalue for this state. If you take the average of all those measurements, you should get the expectation value.
|
WoosterGrad
2018-05-29 21:51:47 |
For the sake of other people studying for the GRE:\r\n\r\nC would be correct if the question asked for the expectation value of the energy-- the number you would get if you took many, many measurements and averaged them.\r\n\r\nHowever, the question asks for a possible value of ONE measurement. A single measurement of the energy will collapse the wave function to a single energy eigenstate.\r\n\r\nThe energy of a state is proportional to the square of the principle quantum number: 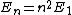 .\r\n\r\nThe principle quantum numbers are 1, 2, and 3 in this superposition, so a single measurement would yield .\r\n\r\nThe principle quantum numbers are 1, 2, and 3 in this superposition, so a single measurement would yield 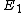 , , 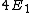 , or , or 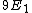 . \r\n\r\nThis reveals choice D as the correct answer. . \r\n\r\nThis reveals choice D as the correct answer.
|
|  | uhurulol
2014-10-19 22:33:27 | Even the solutions here make it sound more complicated than it is. I have not yet taken quantum, so here's how to understand it if you have no quantum knowledge.
All that matters is the equation for 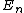 . Plug in 1 for this equation and obtain: . Plug in 1 for this equation and obtain:
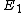 = = 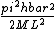 . .
Ergo, 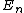 = = 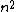 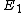 . .
Only choice D accommodates this, as it is the only integer square in the list (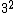 = 9). = 9).
Hope this helps. |  | sina2
2013-09-04 00:56:11 | I think the answer is C. And this is the solution:
http://i.imgur.com/ZqnlRI0.png |  | mpdude8
2012-04-20 21:15:58 | Here's what ETS did on this one: they knew the answer would be trivial if they only gave you what you needed (the expression for E), so they gave you the other crap to make you think it mattered. |  | anmuhich
2009-03-14 13:49:30 | As others have said but I'll state differently...the key word is MEASUREMENT. This indicates that if you were able to open the box and "see" the energy of the particle then you would have to see one of the energies corresponding to an energy eigenvalue of the system. The expectation value is a statistical analysis of the system and is not a real energy value of the system. An analogous situation would be like pulling three numbers out of a bag let's say 1, 3 and 6. Their average (aka expectation value) is 3.33, but you can't pull 3.33 out of the bag. Pulling a number out of the bag is analogous to taking a measurement, you can only pull out 1, 3 or 6. This is a fundamental idea in quantum mechanics but it can be tricky because we spend a lot of time computing expectation values for a composition of eigenstates.
woohao
2015-10-20 14:39:47 |
I agree with Anmuhich, the word MEASUREMENT is very important.
|
|  | ericimo
2007-11-01 15:05:07 | All you need to know is 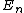 . The rest is given by ETS to try and make you overthink it and skip it. All you see is a scary quantum question when it's just monkey work. . The rest is given by ETS to try and make you overthink it and skip it. All you see is a scary quantum question when it's just monkey work.
It's apparent from the given 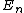 that that 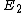 = = 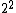 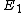 = 4 = 4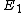 and equally apparent that and equally apparent that 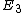 = 9 = 9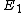 and so on. and so on.
If it's not obvious to you...plug and chug n=1,2,3..., and you see that D works for n=3 which is reason enough to choose it.
ericimo
2007-11-01 15:12:26 |
probably what yosun was getting at, but people didn't seem to be getting it.
|
|  | YeonPil
2007-10-16 05:19:40 | I think, We should suppose that Hy(Psi) = E_n y is correct. If y is not eigenstate, we can not get a E_n.
Therefore, I can get values only such as E1 , 4E1, 9E1, 16E1.........
I agree with author. |  | kevglynn
2006-11-03 08:25:01 | The above comments point out that people commonly mix up concepts within phrases such as "possible energy measurements"; "expectation values"; and "probability of finding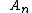 where A is some eigenvalue." Remember what they mean physically and then the math makes sense. It's simple stuff, too, so everyone should pick up these easy points. where A is some eigenvalue." Remember what they mean physically and then the math makes sense. It's simple stuff, too, so everyone should pick up these easy points. |  | Healeyx76
2006-11-02 16:32:05 | Um, the answer is indeed (D), 9E_1 according to the testbook.
a
I get the same conclusion due to the E measurement being dependent on n^2. The only possible solution as a multiple of the ground stte E1 is 9E1 (for state #3)
It seems like for this one they give you a lot of unnecessary info. |  | cailh
2006-10-28 06:46:49 | the answer is c
==1/14*
=1/14*(1+16+81)E1=7E1
beddi
2007-06-13 14:10:10 |
I also think so. Is the solution wrong?
|
deimos
2007-08-27 15:16:10 |
This is the expectation value of the energy. If you were to make a large number a measurements, they would average to that value. In this case we are only concerned with one measurement.
|
odsan
2015-12-18 13:00:12 |
I agree...\r\nThe correct solution is 7E1
|
|  | lolo
2006-10-28 01:45:27 | Or may be you use the difference between "measurement" and "mean value"? |  | lolo
2006-10-28 01:43:15 | 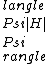 =1/14(+4etc) =1/14(+4etc) |  | lolo
2006-10-28 01:37:57 | This solution is absolutely wrong. Three eigenstates, corresponding to different eigenvalues are mixed. Of course, this function is still an eigenfunction, but the square dependence on n doesn't exist anymore. For example, take a square spin operator S^2. Take two eigenfunctions: singlet and triplet ones. Their linear combination is still an eigenfunction of the operator, but the eigenvalue is not S(S+1) anymore. This happens because we mix functions from the subspaces, corresponding to different eigenvalues.
Moreover, a given function here, is also normalized to unity, so following the elementary quantum mecanics, we get
=1/14{+4etc}
Blake7
2007-09-19 06:33:58 |
The point is not to argue with ETS.
The point is to understand what they are looking for, which (in all my experience) is eventually explicable, and get a good score.
|
gryphia
2008-11-03 20:52:41 |
The point is:rnThe wavefunction is constructed out of a set of eigenstates of the hamiltonian. When you measure the particle, the wavefunction you measure will be one of those eigenfunctions. That means that the energy you measure will be the energy associated with one of those eigenstates. Those energies go as 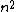 , so the only possible energies you can measure are , so the only possible energies you can measure are 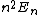 . The only perfect square in the choices we are given is answer d. Thus d is the correct answer. That it corresponds to one of our eigenstates is essential, of course, and if we look at the original function we notice that we have a . The only perfect square in the choices we are given is answer d. Thus d is the correct answer. That it corresponds to one of our eigenstates is essential, of course, and if we look at the original function we notice that we have a 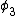 , so everything is good. , so everything is good.
|
|  | lolo
2006-10-28 01:29:17 | |  |
|
|
|
|
The Sidebar Chatbox...
Scroll to see it, or resize your browser to ignore it... |
|
|
|
